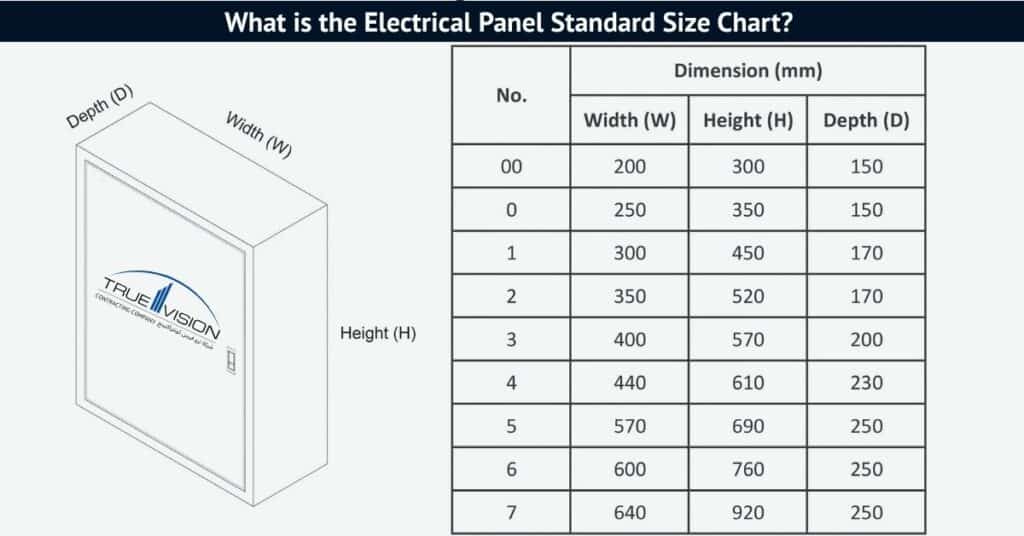
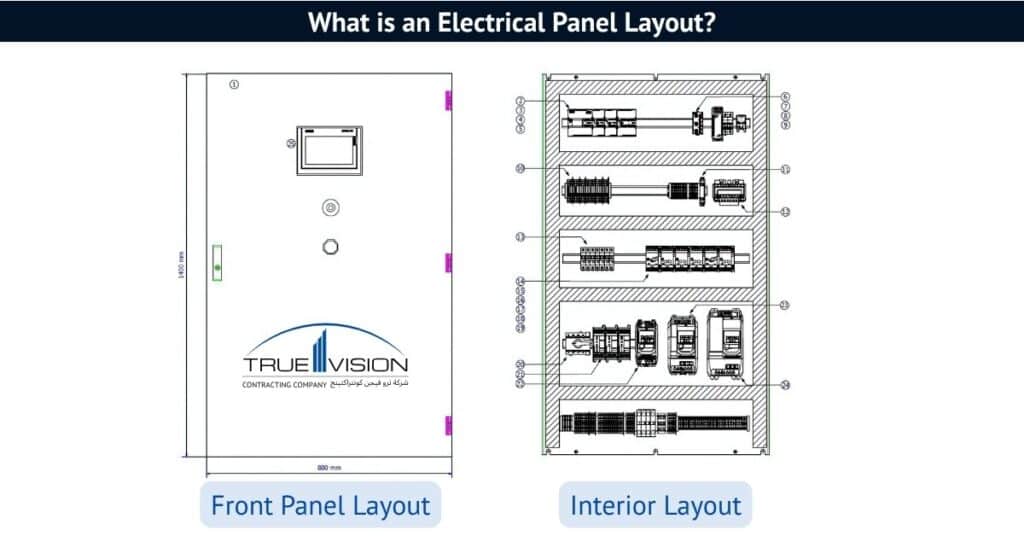
Electrical Panel? Components, Types, Work, Importance, Price
An electrical panel works like the brain of a building’s power system. It takes electricity from the main source and sends it safely to different circuits. In homes, factories, or offices, it protects the system from short circuits or overloads. A well-performing panel is important for safe and efficient electricity use.