DDC Panel: Work, Specs, Components, Application, Size, Price


Meshal Alghomiz is an electrical content writer with a background in Electrical Engineering and affiliation with the Technical and Vocational Training Corporation. He specializes in simplifying complex electrical concepts for technical audiences.
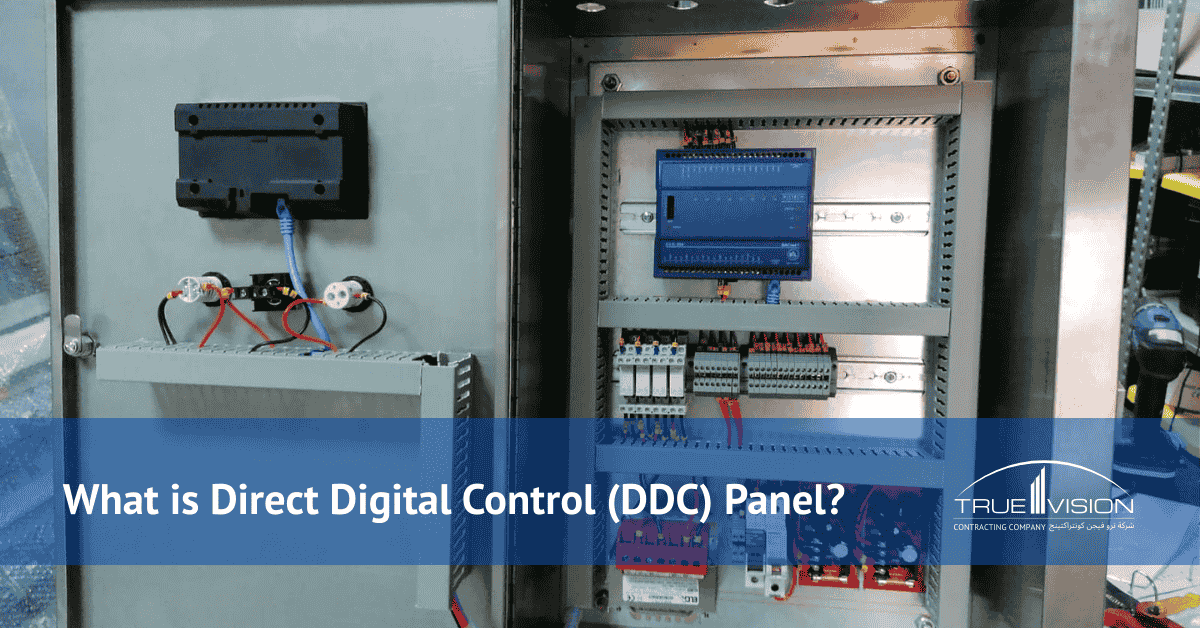
Direct Digital Control (DDC) panels are the backbone of modern building automation. They utilize digital control technology and signals to connect sensors, controllers, and output devices, thereby creating an intelligent HVAC control system that manages heating, ventilation, air conditioning (HVAC), lighting, and security.
The Panel collects real-time data through control panel sensors, processing it instantly with digital microcontrollers and triggering automated responses. DDC panels enhance comfort, reduce energy costs, and minimize maintenance.
The full form of DDC is Direct Digital Control. A DDC panel functions as the central controller in modern building automation systems. It collects real-time data from electronic sensors and manages equipment such as HVAC, lighting, and safety systems. By enabling precise digital control, DDC panels enhance comfort, safety, and energy efficiency in buildings.
The full form of DDC in HVAC is Direct Digital Control. These panels focus specifically on heating, ventilating, and air-conditioning systems. They serve as command centers for climate control equipment throughout buildings.
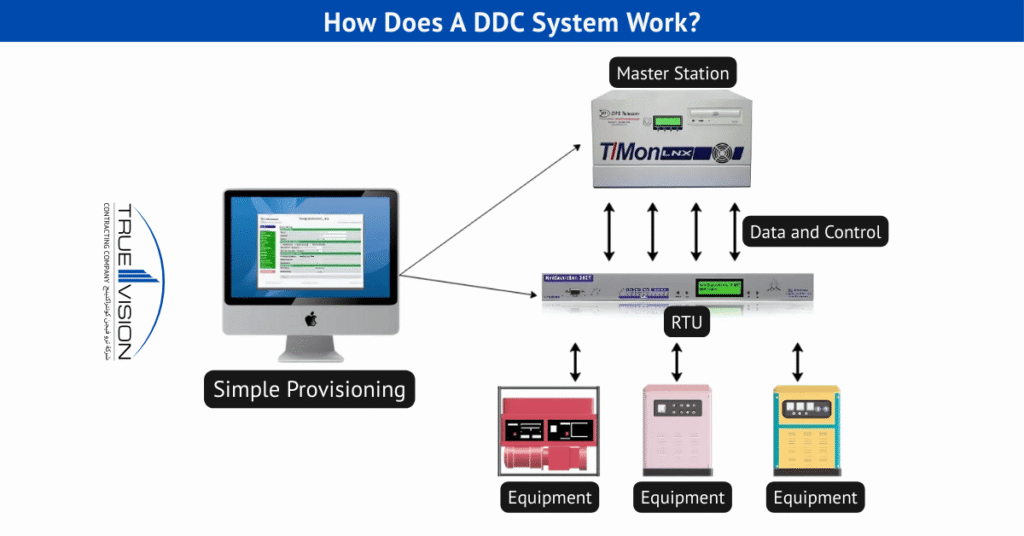
A Direct Digital Control (DDC) system uses a continuous feedback loop to optimize building performance. Input/output devices such as temperature sensors, pressure monitors, and occupancy detectors gather real-time data, which DDC controllers analyze against pre-programmed set points.
Based on the analysis, output signals are sent to devices like motors, valves, and dampers to adjust airflow, temperature, and pressure with precision. A programmed sequence operation ensures systems start and shut down in the correct order, protecting systems and improving reliability.
When integrated across a communication network, multiple DDC panels coordinate building-wide automation strategies, delivering comfort, energy efficiency, and reduced operating costs.
The primary function of Direct Digital Control (DDC) is to automatically monitor and control building systems such as HVAC, lighting, and security using digital computers and microprocessors.
DDC systems work by:
This process ensures buildings maintain comfort, safety, and energy efficiency while reducing manual intervention and operating costs.
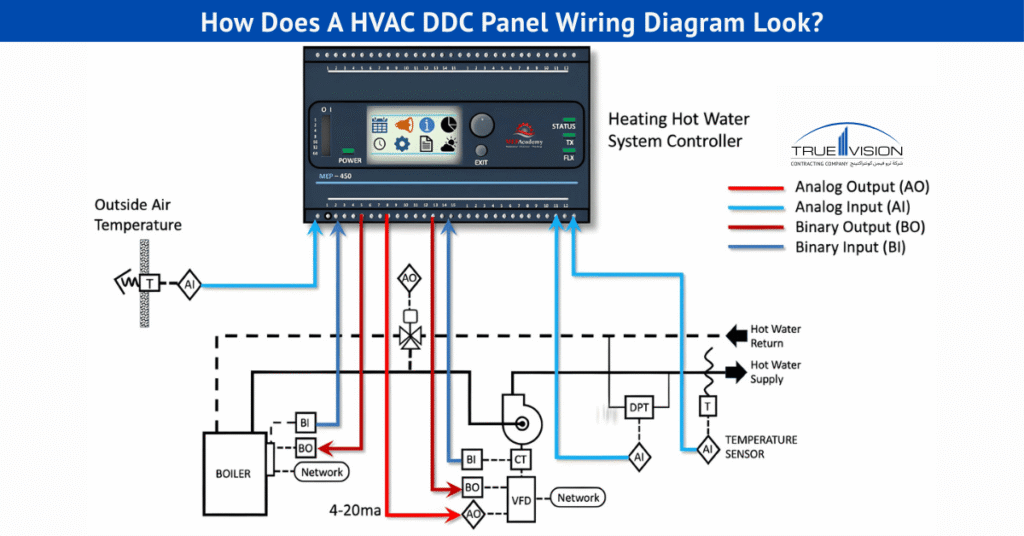
Refer to the diagram below, which clearly illustrates all electrical connections for a DDC panel wiring setup.
A DDC (Direct Digital Control) panel in a Building Management System (BMS) is a hardware unit that houses a programmable controller, input/output (I/O) modules, and communication interfaces. It functions as the control hub for automated building operations, including HVAC, lighting, and energy management.
No, DDC (Direct Digital Control) and BMS (Building Management System) are not the same, but they are related technologies. DDC refers to the control hardware and software that directly operate building equipment. BMS encompasses the entire management infrastructure.
A complete BMS includes multiple DDC panels connected through communication networks. The manufacturer integrates DDC technology as the foundation layer.
DDC provides real-time equipment control and local optimization. BMS adds higher-level functions like energy reporting, enterprise integration, and facility-wide optimization. Modern cloud-based BMS platforms coordinate multiple buildings, each containing numerous DDC panels.
| Category | Specification |
|---|---|
| System Type | Direct Digital Control (DDC) panel for HVAC & BMS integration |
| Controller | Microprocessor-based, programmable, supports multi-loop control |
| Memory | ROM/RAM for control logic storage, real-time processing |
| Inputs |
Analog Inputs (AI): Temperature, humidity, pressure sensors Digital Inputs (DI): On/Off status, alarms |
| Outputs |
Analog Outputs (AO): Modulating dampers, valves Digital Outputs (DO): Fans, pumps, relays |
| Communication Protocols | BACnet, Modbus, LonWorks (open protocol support) |
| Networking | Compatible with BMS and third-party systems |
| Power Supply | 24V AC/DC or 120/240V AC (depending on configuration) |
| Environmental Ratings |
Operating Temp: -40°C to +71°C (-40°F to +160°F) Humidity: up to 95% RH, non-condensing |
| Enclosure | NEMA 1 (indoor) or NEMA 4/12 (industrial/harsh environments) |
| Protection Features | Dust-proof, moisture-resistant, tamper-protected enclosure |
| Applications | HVAC equipment control, energy efficiency optimization, safety & comfort monitoring |
DDC systems contain three main component categories: input devices, controllers, and output devices. The communication infrastructure connects all components through networks. This enables data exchange and system coordination.
The manufacturer designs these components to work together while providing flexibility for various applications.
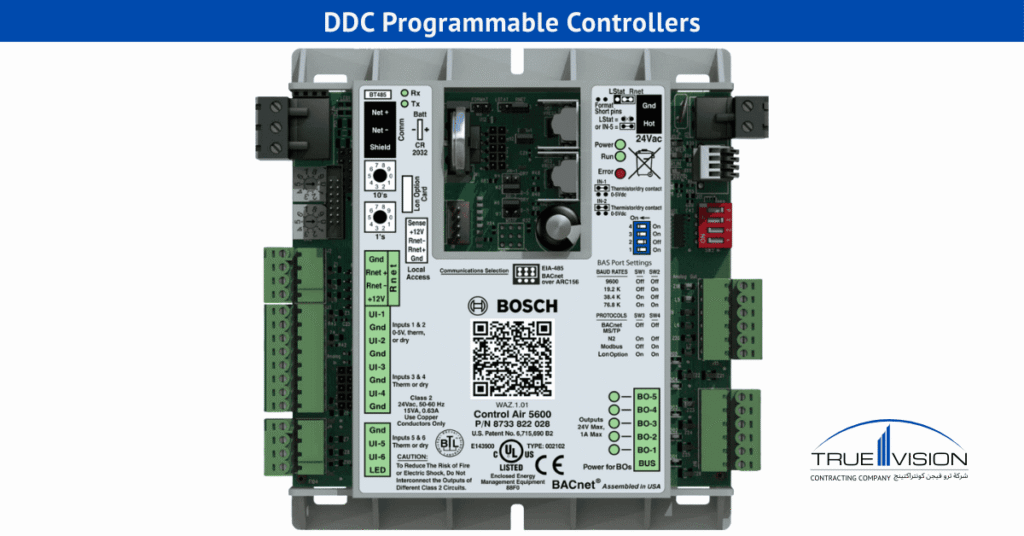
The DDC controller acts as the brain of building automation systems. This central processing unit makes all control decisions and coordinates equipment operations.
Modern controllers use ARM or Intel processors with 1-4 GHz speeds. They include 1-4 GB RAM for running control programs and 8-32 GB flash storage for data logging.
Real-time operating systems ensure precise timing for HVAC equipment. Controllers execute multiple control loops simultaneously without delays.
Programming happens through web browsers or dedicated software. Popular languages include structured text and function blocks.
Most controllers feature Ethernet ports for network connectivity. They support BACnet, Modbus, and proprietary protocols for system integration.
Redundancy options include dual controllers and backup power supplies. This prevents system failures during equipment maintenance.
Input devices collect real-time building data. Temperature sensors monitor air and water temperatures throughout facilities. Different sensor types suit various accuracy requirements and environmental conditions.
Humidity sensors track moisture levels for comfort and air quality control. Pressure sensors monitor air pressure in ducts and water pressure in pipes.
Status inputs provide equipment feedback, including motor operation, valve positions, and alarm conditions. Flow sensors monitor air and water flow rates. Occupancy sensors detect presence in rooms and zones. This enables energy-saving strategies when areas are unoccupied.
Output devices implement physical control actions. Variable frequency drives control motor speeds for fans, pumps, and compressors. This provides energy-efficient operation across varying load conditions.
Actuators operate dampers and valves to control air and water flow. Electric, pneumatic, and electronic types suit different applications.
Relay outputs control on/off devices like pumps, fans, and lighting circuits. Analog outputs provide precise control of modulating devices.
Analog input modules convert sensor signals into digital values for processing. They handle temperature, pressure, and flow measurements.
Standard inputs accept 0-10VDC voltage signals and 4-20mA current loops. Resolution ranges from 12-bit (4,096 values) to 16-bit (65,536 values).
RTD and thermistor inputs measure temperature directly. Three-wire RTD connections provide lead wire compensation for accuracy.
Built-in signal conditioning includes amplification and filtering. This ensures clean signals regardless of cable length or electrical noise.
Calibration features allow zero and span adjustments. Software calibration eliminates hardware potentiometer adjustments.
To understand how building automation works, it’s helpful to look at the different DDC panel systems commonly used.
Primary Control Components
Power Supply Components
Networking & Communication
Protection & Wiring Components
Enclosure & Structure
Temperature sensors connect to specific terminals on analog input modules. Connection methods vary by sensor type.
RTD sensors use three-wire connections:
Thermistor sensors require two-wire connections:
Use shielded cable for all temperature connections. Connect the shield to the ground terminal in the electrical panel to prevent interference.
Wire gauge depends on cable length. Use 18 AWG for runs up to 1,000 feet and 16 AWG for longer distances.
Terminal torque specifications prevent loose connections. Follow manufacturer recommendations, typically 7-10 inch-pounds for small terminals.
DDC panels serve multiple industries with specialized control needs.
Healthcare facilities require precise environmental control. Operating rooms maintain ±2°F temperature control and specific humidity levels. Clean rooms need constant pressure monitoring and HEPA filter management.
Educational institutions focus on energy savings. DDC panels reduce consumption by 20-30% through occupancy scheduling and demand limiting. Campus-wide coordination optimizes multiple buildings simultaneously.
Data centers demand cooling precision. Server rooms require ±1°F temperature control with redundant cooling systems. DDC panels monitor power usage effectiveness (PUE) ratios.
Manufacturing plants need process control integration. DDC panels coordinate HVAC systems with production equipment to maintain quality standards. Clean room applications require particle monitoring.
Commercial offices prioritize tenant comfort and energy costs. Zone-based control allows individual floor management while maintaining overall building efficiency.
Retail stores use DDC for customer experience. Automatic scheduling adjusts conditions for store hours while reducing after-hours energy consumption.
DDC panel installation follows specific steps for safe, reliable operation.
The planning phase starts with reviewing electrical drawings. Verify power requirements, panel locations, and field device connections before installation begins.
Panel mounting requires proper wall supports or floor pads. Maintain 36-inch clearance in front and 6 inches on sides for access. Indoor locations protect equipment from the weather.
Power connections need qualified electricians to follow the NEC codes. Install proper circuit breakers and disconnects. Separate high-voltage power from low-voltage control circuits.
Field wiring connects sensors and actuators to I/O modules. Use manufacturer-specified cable types and maintain proper wire separation. Label all connections clearly.
Communication wiring links panels to central systems. Install network cables per TIA standards using appropriate cable categories for data rates.
System commissioning verifies proper operation. Test all input/output points, communication links, and control sequences. Document settings and calibration values.
A DDC (Direct Digital Control) panel doesn’t usually come in “fixed standard sizes” like an appliance. It’s built based on the project requirements, such as the number of input/output points, field devices, and control sequences.
Panel depth varies from 6 inches for basic units to 20 inches for complex configurations with multiple controllers and communication modules.
The price of a DDC panel typically ranges from SAR 11,000 – 280,000, depending on the size, complexity, and application.
Financing options include leasing and energy service contracts. These reduce upfront costs while providing guaranteed performance levels.
DDC panels are the smart backbone of building automation, combining advanced DDC control systems and precise inputs for efficient management across industries. With sizes and prices to fit any facility, they offer measurable energy savings and long-term value. Choosing the right DDC panel improves comfort, reliability, and cost-effectiveness in any environment.
Sale Team Need help? Call us 24/7
Office Contact
Complain & Support Team
Connect with support with email
Submit your inquiry
Office time
Office Location in Saudi Arabia