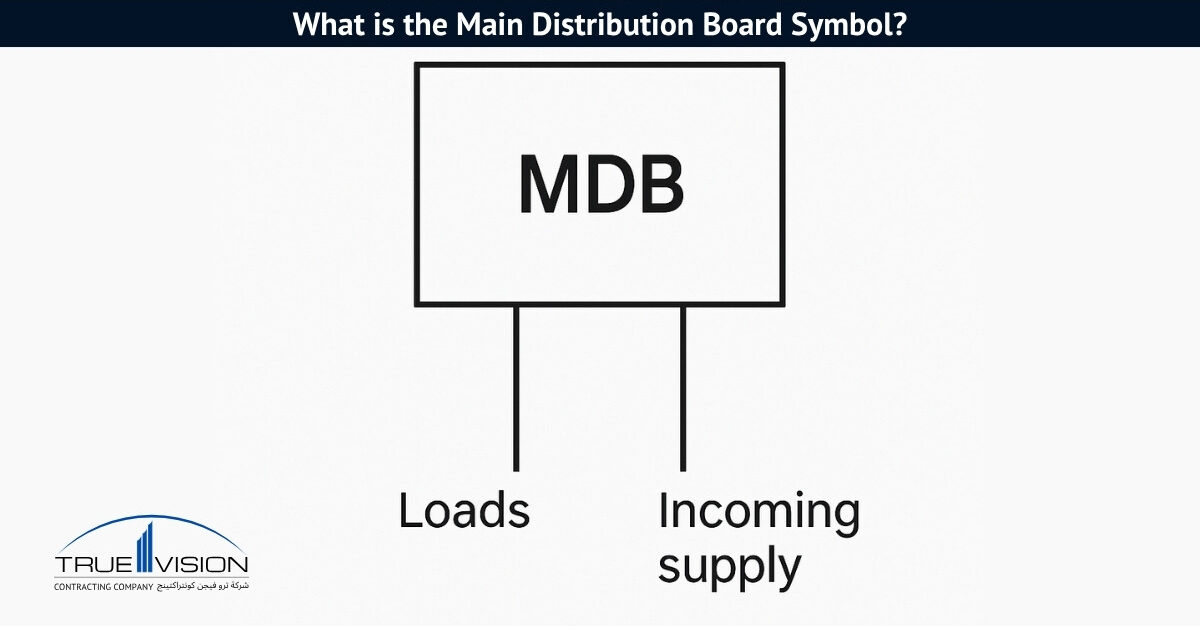
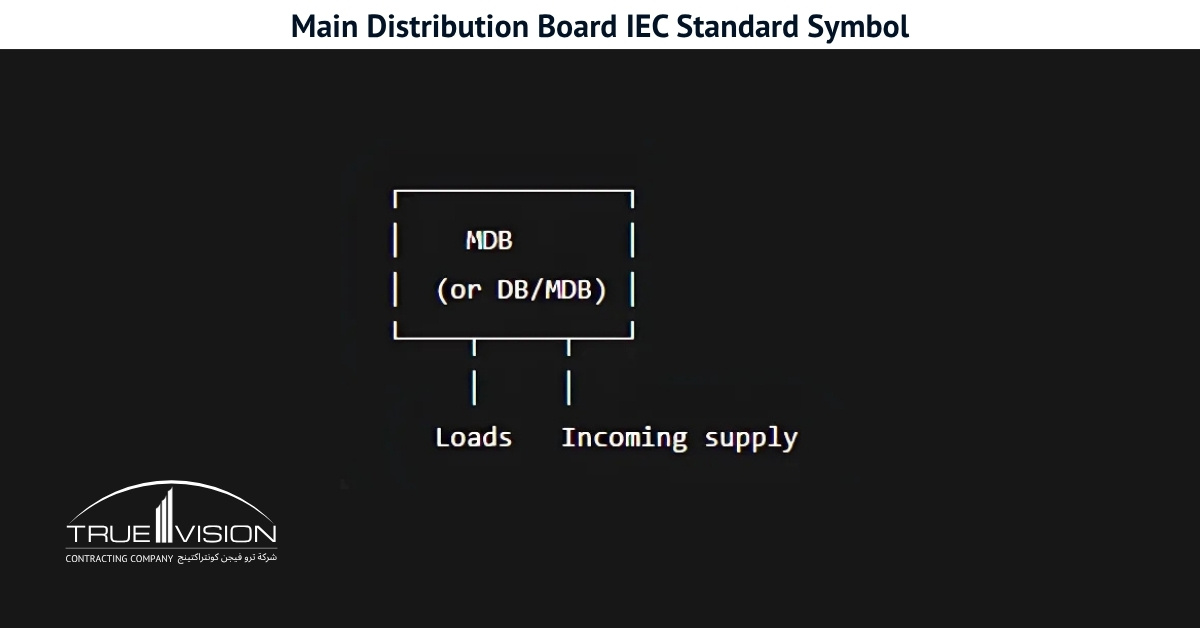
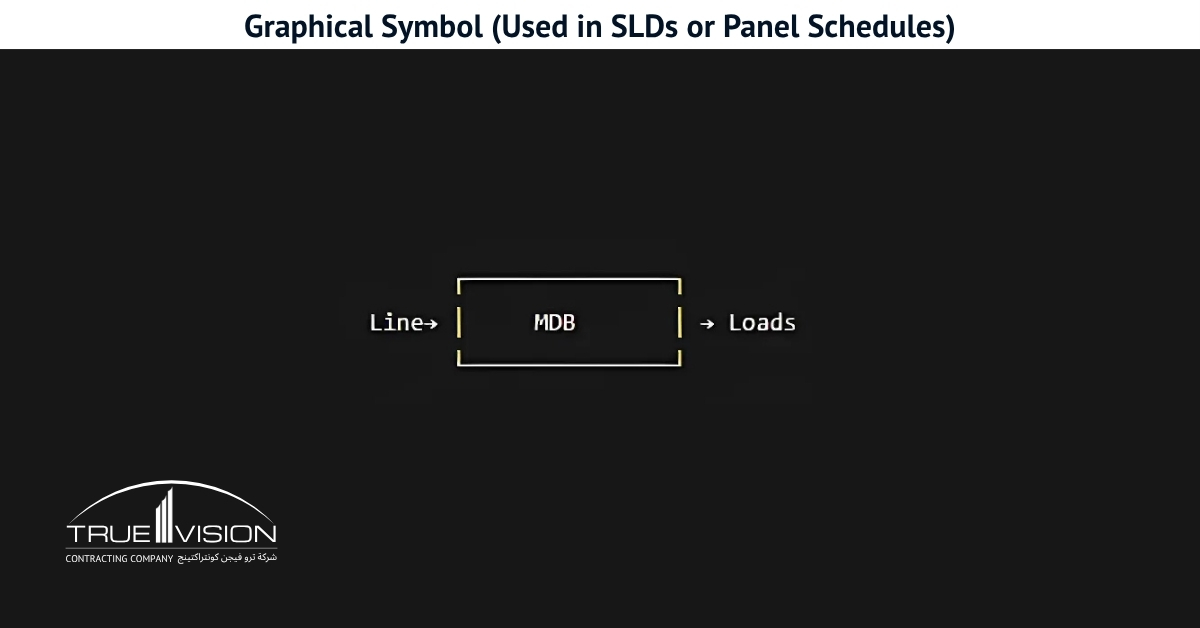
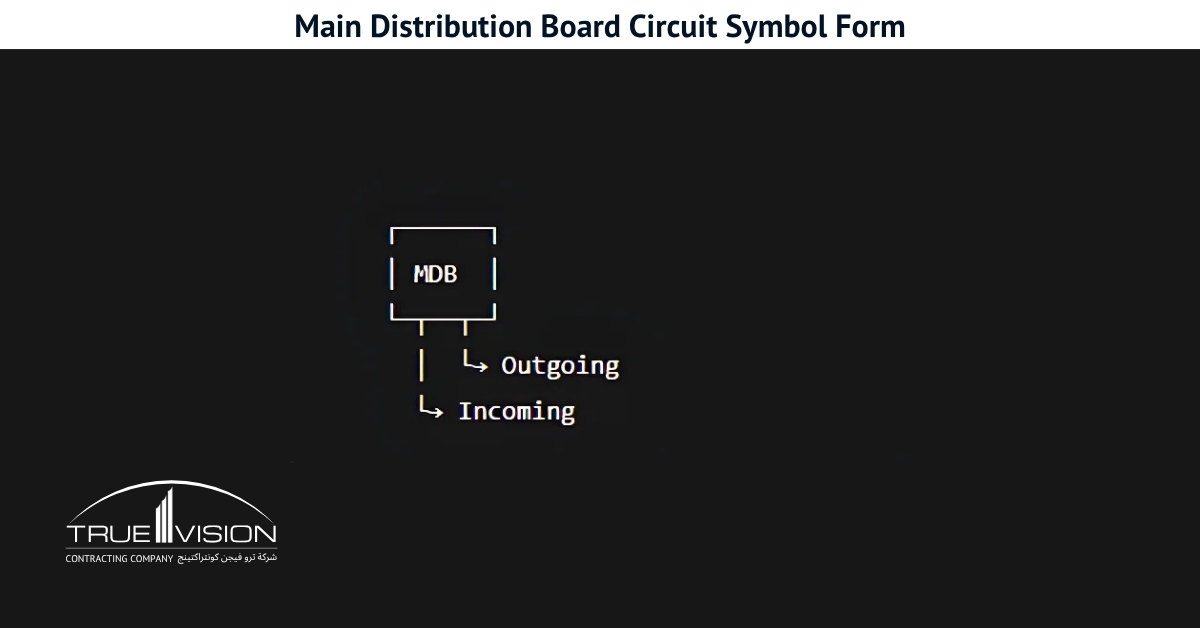
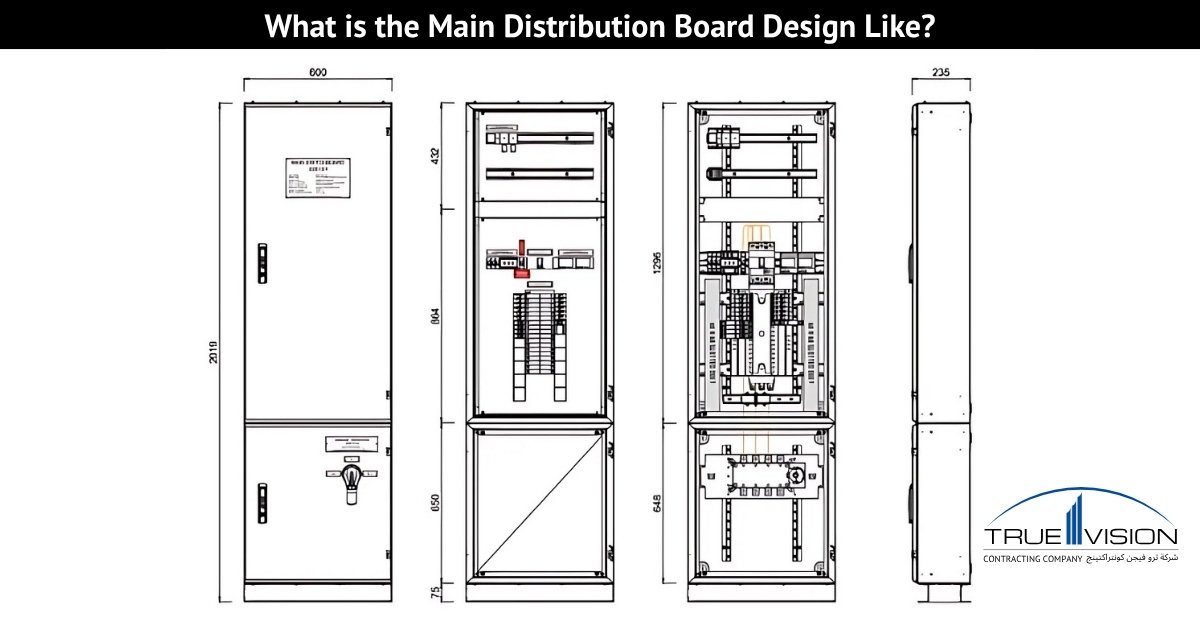
MDB Panel: Types, Components, Size, Design, Price, Service
Main Distribution Boards (MDBs) play a crucial role in any power system by distributing electricity from the transformer’s main supply to various circuits. Used across homes, offices, and industrial sites, these boards vary in size, capacity, and configuration. Before selecting one, it’s important to understand your system’s load requirements and ensure the MDB meets all safety and compliance standards.