PLC Panel: Components, Code, Work, Design, Specification, Price
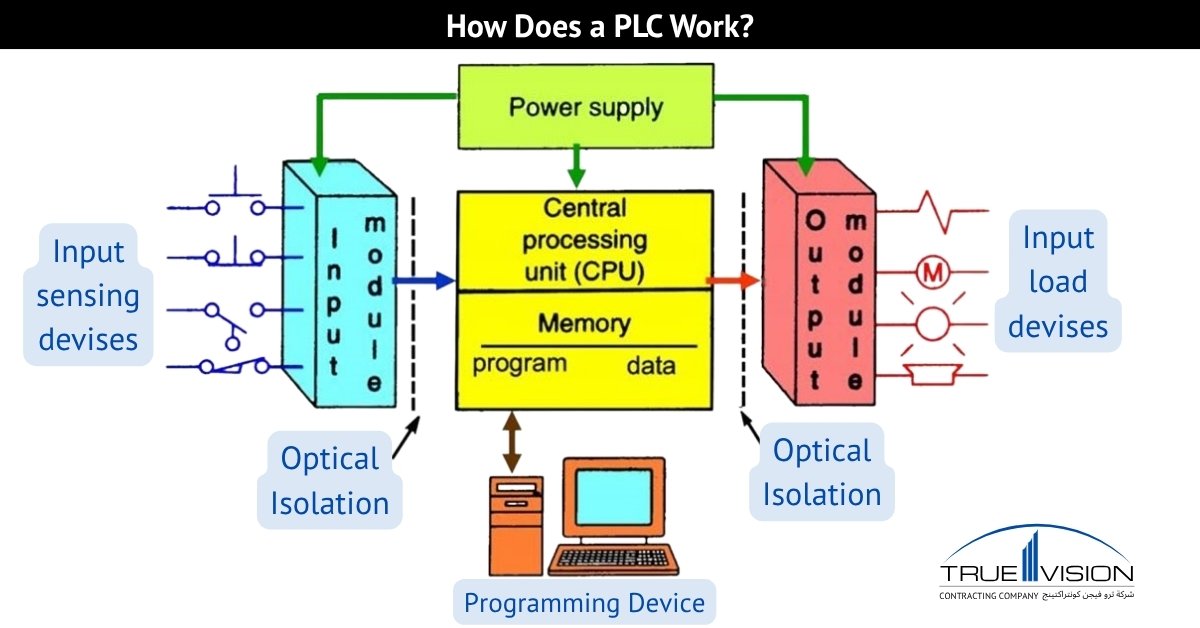
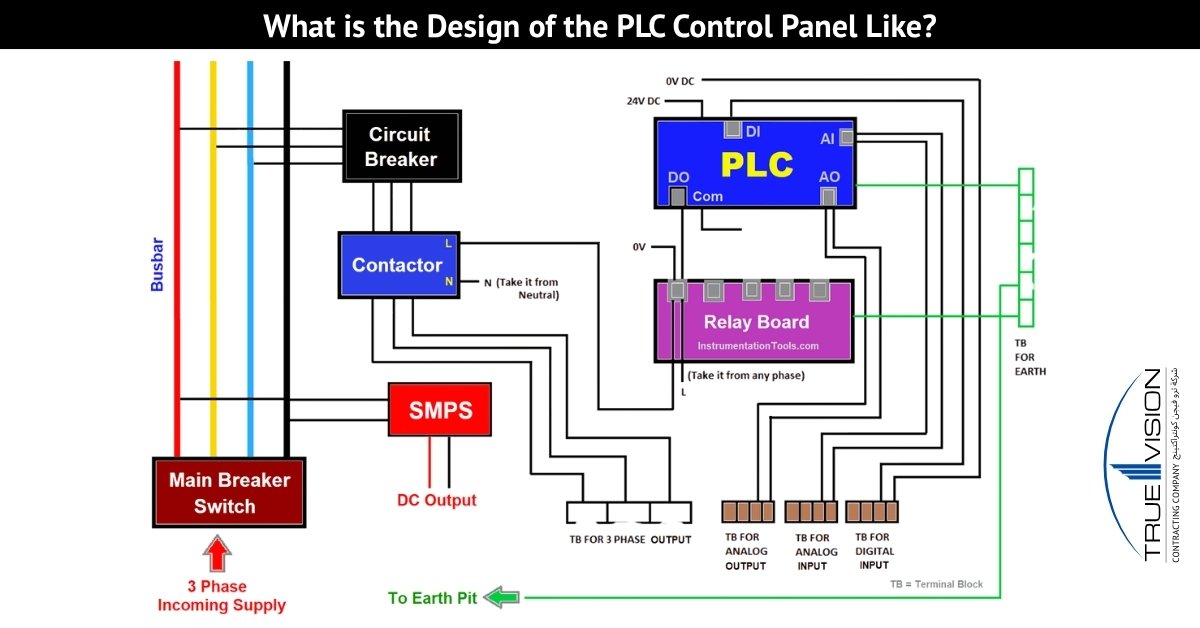
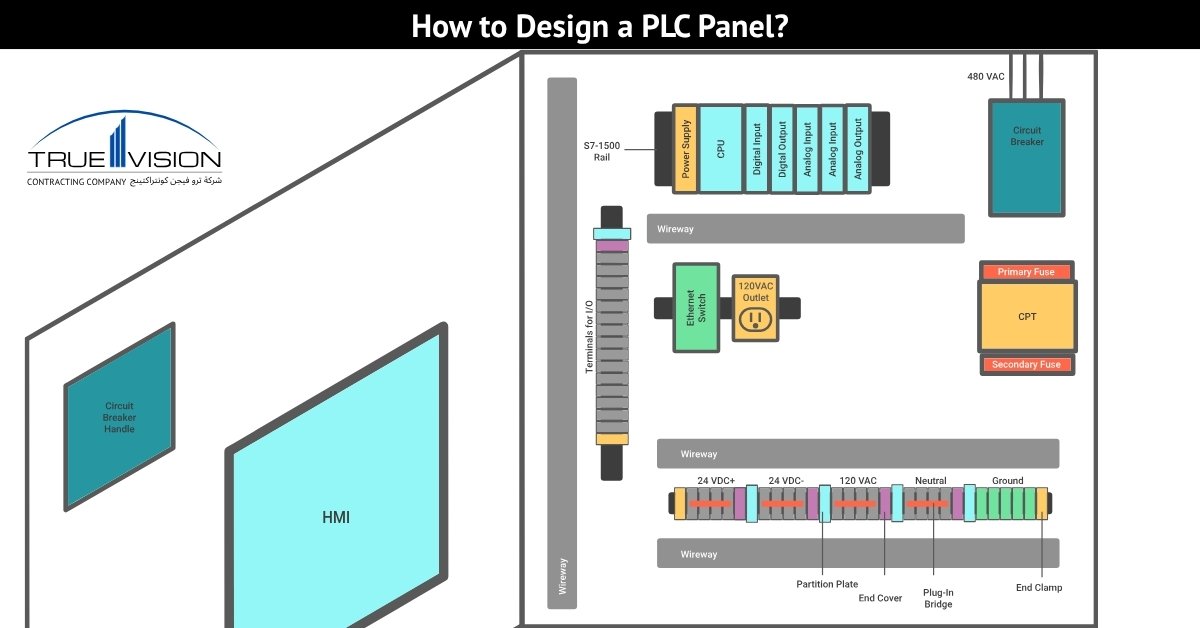
A Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) panel is the backbone of industrial automation, easily integrating hardware, software, and design to control and monitor complex processes. Built to withstand harsh industrial environments, PLC panels are designed with precision to ensure efficiency, reliability, and scalability. From process automation control to real-time monitoring, these panels play a critical role in reducing manual intervention and enhancing operational safety.